Contact Us | Sign In
Media Converter Overview
What is a Media Converter?
Media converters are flexible and cost-effective devices for implementing and optimizing fiber links in all types of networks. The most common type of media converter is a device that functions as a transceiver converting the electrical signal used in copper Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) network cabling into light waves used in fiber optic cabling.
Fiber optic connectivity is necessary when the distance between two network devices exceeds the transmission distance of copper cabling. Copper-to-fiber conversion using media converters enables two network devices with copper ports to be connected over extended distances via fiber optic cabling.
Media converters are available as Physical Layer or Layer 2 switching devices, and can provide rate-switching and other advanced switching features like VLAN tagging. Media converters are typically protocol specific and are available to support a wide variety of network types and data rates.
Media converters can also convert between wavelengths for Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) applications.
Deployed in Enterprise, Government, Data Center, and Telecom Fiber to the x networks, media converters have become the Swiss army knife of networking to enable connectivity and fiber distance extension.
The Benefits of Media Converters
Network complexity, demanding applications, and the growing number of devices on the network are driving network speeds and bandwidth requirements higher and forcing longer distance requirements within the Local Area Network (LAN). Media converters present solutions to these problems, by allowing the use of fiber when it is needed, and integrating new equipment into existing cabling infrastructure. Media converters provide seamless integration of copper and fiber, and different fiber types in Enterprise LAN networks. They support a wide variety of protocols, data rates and media types to create a more reliable and cost-effective network.
Demands on the Network are Increasing:
- LANs and WANs are converging, and networks are growing in physical area
- Budget constraints are pushing preservation of capital investment in legacy switches and routers
- New network services are driving up bandwidth demand
Solutions Provided by Media Converters:
- Increase network distances by converting UTP to fiber and extending fiber links
- Maintain investments in existing equipment
- Increase the capacity of existing fiber with WDM wavelengths (when used with multiplexers)
New Applications for Media Converters:
- Remotely managed converter and multi-port switch configurations
- Convert WDM wavelengths for bandwidth capacity enhancement
- Enable Fiber-to-the-Desktop
Media converters do more than convert copper-to-fiber and convert between different fiber types. Media converters for Ethernet networks can support integrated switch technology, and provide the ability to perform 10/100 and 10/100/1000 rate switching. Additionally, media converters can support advanced features including VLAN, Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, Port Access Control and Bandwidth Control. These features facilitate the deployment of new data, voice and video to end users. Media converters can provide all these sophisticated switch capabilities in a small, cost-effective device.
Media converters save capital equipment expenditures (CAPEX) by enabling interconnection between existing switches, servers, routers and hubs; preserving the investment in legacy equipment. They also reduce CAPEX by avoiding the need to install new fiber links by enabling WDM technology through wavelength conversion.
Media converters also reduce network operating costs (OPEX) by helping to troubleshoot and remotely configure network equipment that is at distant locations, saving time and money when there is not a network administrator at the distant location.
Media Converters Leverage the Benefits of Fiber Optic Cabling
Fiber can transport more data over longer distances than copper cabling, and increased distances provide the ability to reach more users and equipment. Fiber has complete immunity to electrical interference, and provides higher security than copper cabling because it has no electro-magnetic emission. These characteristics have made fiber an ideal medium for commercial, utility, government and financial networks.
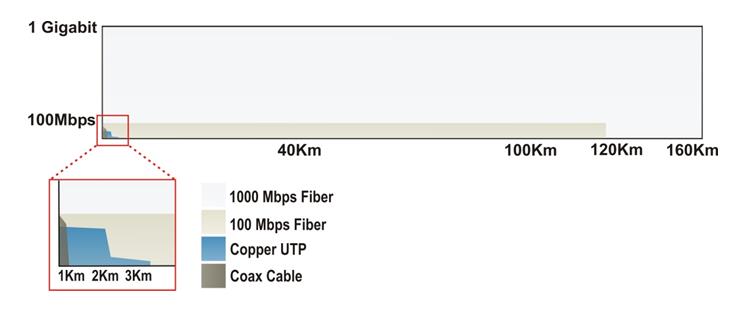
Distances supported by fiber network infrastructure are limited mostly by the optical power, or brightness, supplied by the active interface hardware. Fiber distances can range from 300 meters to 160 kilometers, depending on the type of media converter, cable, wavelength and data rate.
Types of Media Converters
Types of Media Converters
There are a wide variety of copper-to-fiber and fiber-to-fiber media converters available that support different network protocols, data rates, cabling and connector types.

Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
Supporting the IEEE 802.3 standard, Ethernet copper-to-fiber media converters provide connectivity for Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, Gigabit and 10 Gigabit Ethernet devices. Some converters support 10/100 or 10/100/1000 rate switching, enabling the integration of equipment of different data rates and interface types into one seamless network.

Fiber to Fiber Media Converters
Fiber-to-fiber media converters provide connectivity between multimode and single-mode fiber, and between dual fiber and single-fiber. In addition, fiber-to-fiber media converters support conversion from one wavelength to another, including standard wavelengths (1310, 1550) and CWDM wavelengths. Fiber-to-fiber media converters are typically protocol independent and available for Ethernet, and TDM applications.
Media Converters Support a Variety of Network Protocols:
- 10, 100, Gigabit and 10G Ethernet
- 10G OTN
- T1 / E1 and T3 / E3 / DS3>
- SONET (OC-3, OC-12, OC-48 and OC-96)
- Fibre Channel
- Serial RS-232 / 422 / 530
- Protocol Transparent, supporting data rates up to 11.32Gbps
Media Converter Support a Variety of Fiber Cable and Connector Types:
- SFP, SFP+ and XFP Standard Wavelength Transceivers
- SFP, SFP+ and XFP CWDM Transceivers
- ST, SC, LC and MT-RJ Connectors
- Single-mode and Multimode Fiber
- Dual and Single Fiber
Media Converter Support a Variety of Copper Cable and Connector Types:
- Copper RJ-45
- BNC and Mini BNC
- Coax
- UTP Category 4, 5 and 6

Standalone and Chassis-Based Media Converters
Media converters are available as compact standalone units that can be AC or DC powered. Standalone media converters are deployed to convert one copper connection to fiber in a point-to-point deployment.
Chassis-based media converters are plug-in modules that can be installed in a variety of chassis configurations. High-density, rack-mount chassis enable multiple fiber runs from copper switches in a star topology. Compact chassis provide a fiber uplink and multiple copper ports for network edge deployments. Chassis feature multiple power supplies for redundant power protection and data backplanes that provide connectivity between modules for flexible and scalable multi-port deployments.
Unmanaged and Managed Media Converters
An unmanaged media converter simply allows devices to communicate, and does not provide the same level of monitoring, fault detection and configuration as equivalent managed media converters. Connect the devices to the unmanaged media converter and they usually communicate automatically. Unmanaged media converters are simple to use and install. For most unmanaged converters, minimal configuration is required. Basic configuration of duplex modes, auto-negotiation, and crossover can be configured with DIP-switches. Unmanaged media converters provide networking features that can also be configured with DIP-switches such as remote fault indication, fault propagation, and loopback modes.
A managed media converter is typically more costly than an unmanaged media converter; however, a managed converter provides network monitoring, fault detection and remote configuration functionality not available with an unmanaged media converter. These management capabilities provide tangible benefits that reduce operating costs and improve network reliability.

- Remote configuration/provisioning reduces trips to edge equipment
- Performance monitoring provides warnings on potential problems
- Fault management proactively monitors for network problems and quickly isolates network faults
- Intuitive software interface simplifies provisioning of complex networks and services
Managed media converters require additional hardware to enable SNMPv1, SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 management. This can be a management module
installed in the same chassis as managed media converters, or a media converter with integrated management capabilities.
Copper to Fiber
How to Use Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
Copper-to-fiber media converters are compact devices that provide seamless integration of copper and fiber cabling. They can be deployed in a variety of networks, and typically provide point-to-point fiber connectivity in copper networks.
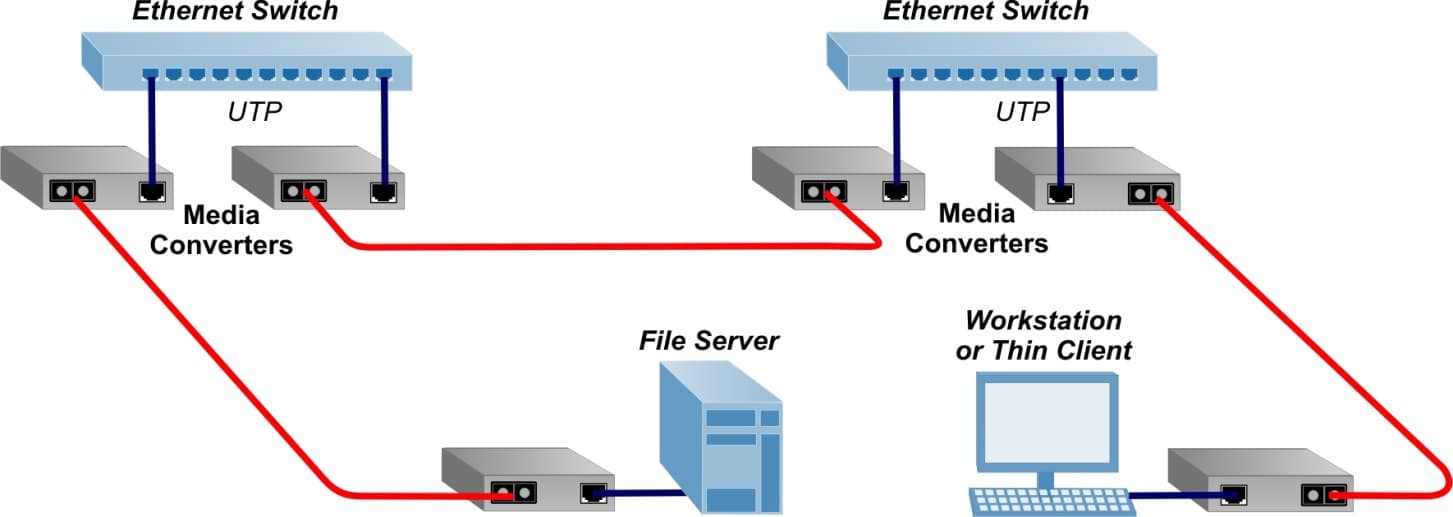
Ethernet Point-to-Point Media Converter Application
This application example demonstrates how to deploy media converters and provide seamless integration of different Ethernet cabling media. Ethernet copper-to-fiber media converters support a variety of cabling and connectors, different network protocols, and data rates from 10 Mbps to 10G.
A pair of copper-to-fiber media converters is used to connect two copper switches via fiber. A workstation and a server are also connected to the network using pairs of copper-to-fiber media converters.
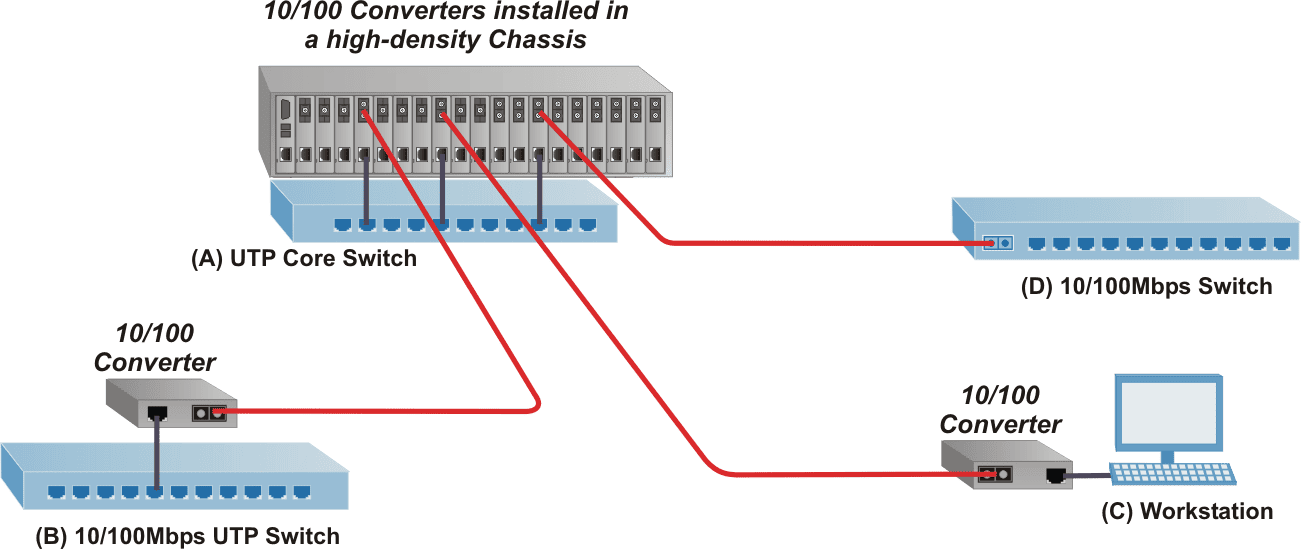
Ethernet Campus Fiber Media Converter Application
In this application example, 10/100 media converters are installed in a redundant power chassis for high-density fiber distribution from UTP switch equipment (A) at the network core. A UTP workgroup switch (B) is connected via fiber to the network core with a standalone 10/100 media converter. Another 10/100 converter enables fiber connectivity to a PC UTP port in a fiber-to-desktop application (C). An Ethernet switch (D) is connected directly via fiber to the media converter module at the network core. This network application example can support 10/100, 10/100/1000 and 10G data rates.
10G Ethernet Media Converter Application
10G media converters provide a variety of 10G data center connectivity solutions, including resolving interface disparities between equipment with 10GBASE-T RJ-45 ports and existing rack servers or switches with fiber optic ports. Architecture changes such as migrating from Top of Rack to End of Row can present cabling challenges when extending network distances from racks of servers.
In this application, fiber cabling is used to extend distances between 10G switches and servers. A Redundant Power Chassis with 10G Copper-to-Fiber plug-in media converters is used to convert the CAT-6A cabling from the RJ-45 ports on the aggregation switch to fiber.
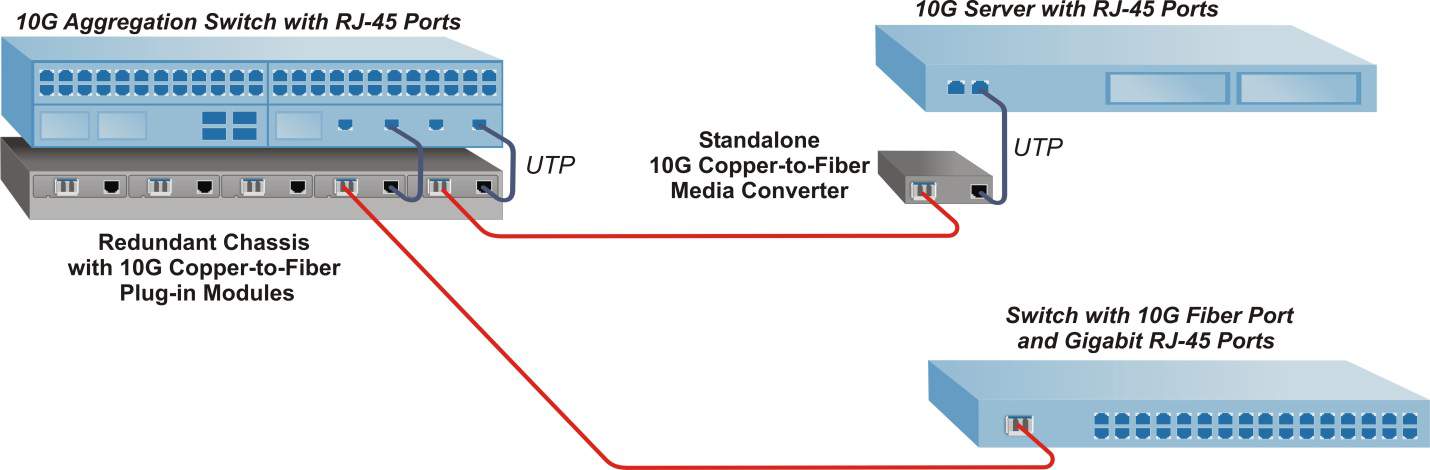
At the other end of the first fiber run, a standalone 10G Copper-to-Fiber converter is used to convert the fiber back to copper for connectivity to a 10G server with RJ-45 ports. The second fiber run connects directly to a fiber port on a 10G switch.
The 10G Copper-to-Fiber converter supports CAT-6A cabling (up to 100 meters) to extend distances to servers, switches and patch panels. For CAT-6A cabling links less than 30 meters, 10GBASE-T Short Reach mode can be used to conserve energy by reducing power and cooling requirements.
How to Use TDM Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
T1 and T3 copper-to-fiber media converters provide cost-effective demarcation extension of traditional TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) telecom protocols with fiber optic cabling
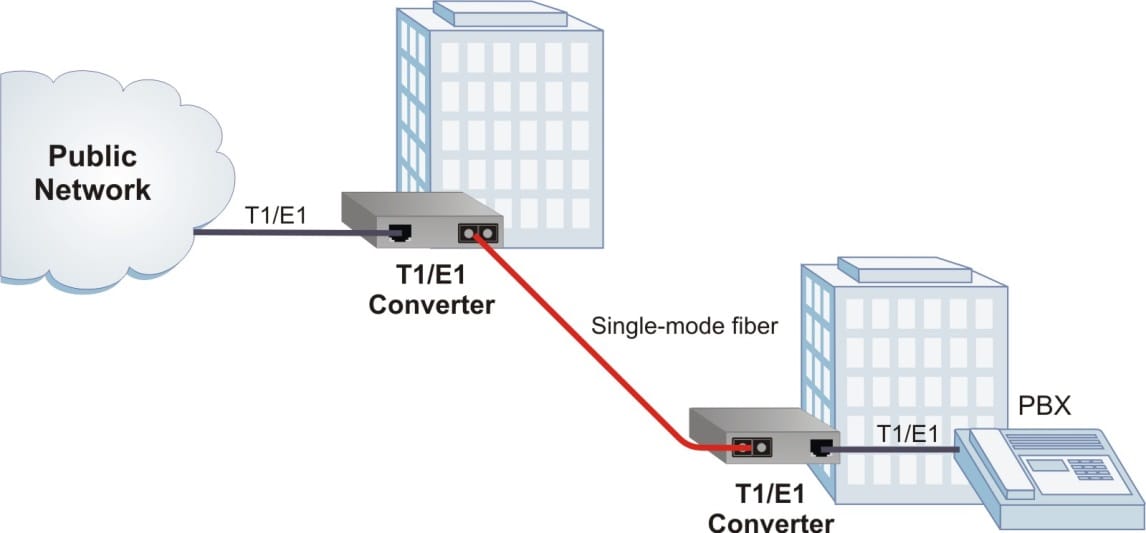
T1 Media Converter Application
T1 and T3 converters operate in pairs extending distances of TDM circuits over fiber, improving noise immunity, quality of service, intrusion protection and network security. They are typically deployed to provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for extending telecom demarcation points across a business complex or up a high-rise building using fiber optic cabling.
In this application, a pair of T1/E1 media converters is used to extend the demarcation point (hand-off from the Service Provider) to another tenant building with fiber. A variety of fiber types can be deployed, and fiber links can be extended up to 120km using single-mode fiber.
How to Use Serial Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
Serial-to-fiber converters provide fiber extension for serial protocol copper connections. They can automatically detect the signal baud rate of the connected Full-Duplex serial device, and support point-to-point and multi-point configurations.
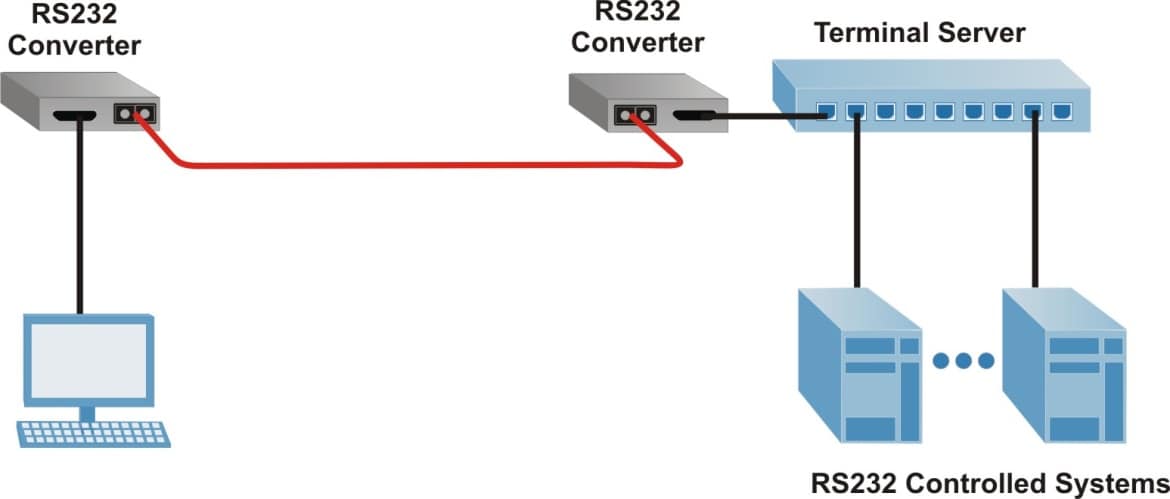
RS-232 Media Converter Application
RS-232 fiber converters can operate as asynchronous devices, support speeds up to 921,600 baud, and support a wide variety of hardware flow control signals to enable seamless connectivity with most serial devices. In this example, a pair of RS-232 converters provides the serial connection between a PC and Terminal Server allowing access to multiple data devices via fiber.
Fiber to Fiber
How to Use Fiber-to-Fiber Media Converters
Fiber-to-fiber media converters provide connectivity between multimode (MM) and single-mode (SM) fiber, and between dual fiber and single-fiber. In addition, they support conversion from one wavelength to another. Fiber-to-fiber media converters are normally protocol independent and available for Ethernet and TDM applications.
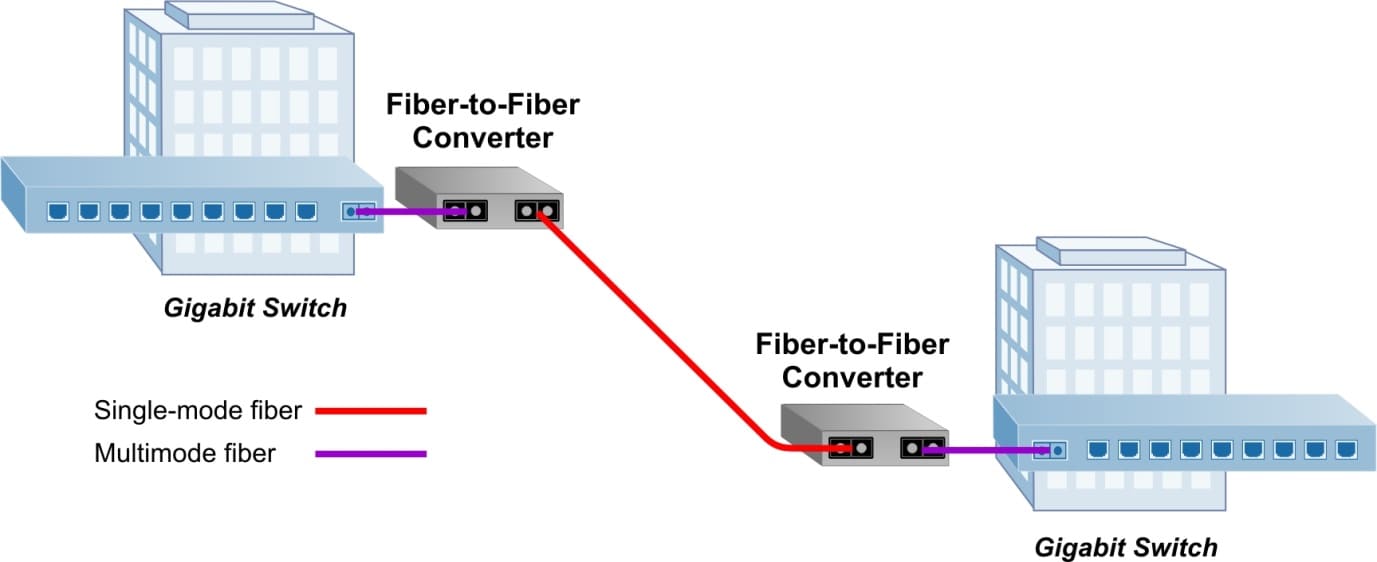
Multimode to Single-mode Fiber Media Converter Application
Enterprise networks often require conversion from MM to SM fiber, which supports longer distances than MM fiber. Mode conversion is typically required when: 1) lower cost legacy equipment uses MM ports, and connectivity is required to SM equipment, 2) a building has MM equipment, while the connection to the service provider is SM, 3) MM equipment is in a campus building and SM fiber is used between buildings.
A fiber-to-fiber media converter can extend a MM network across SM fiber with distances up to 160km. In this application, two Gigabit Ethernet switches equipped with MM fiber ports are connected utilizing a pair of Gigabit fiber-to-fiber converters, which convert the MM fiber to SM and enable the long distance connection between the switches.
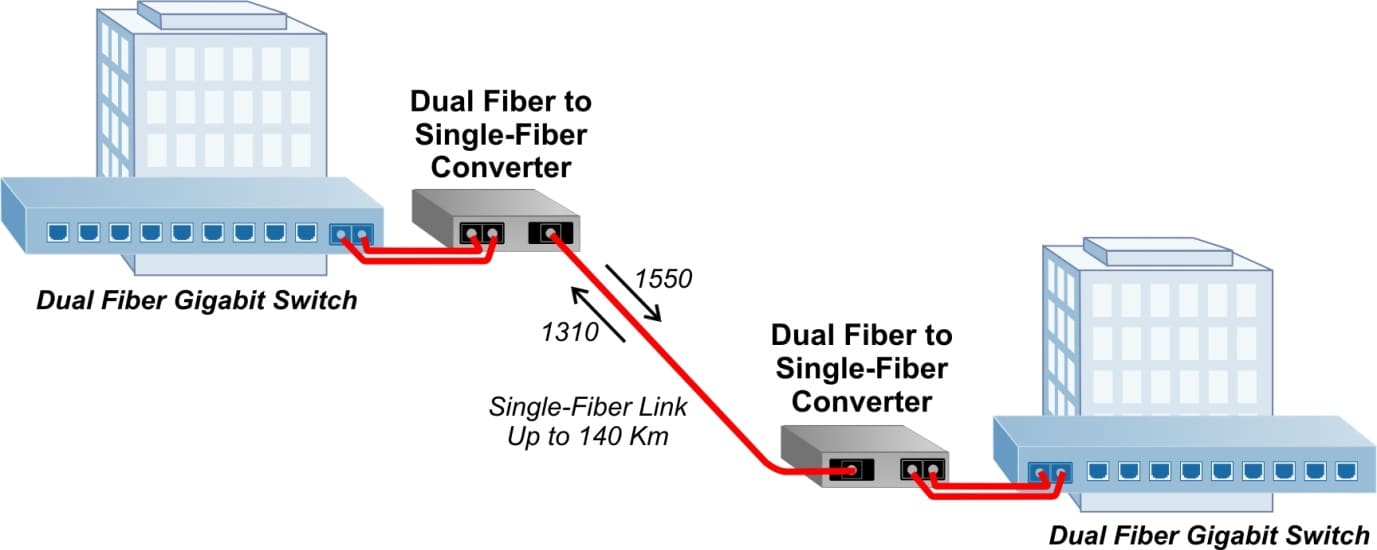
Dual Fiber to Single-Fiber Media Converter Conversion
Enterprise networks may also require conversion between dual and single-fiber, depending on the type of equipment and the fiber installed in the facility. Single-fiber is single-mode and operates with bi-directional wavelengths, often referred to as BIDI. Typically BIDI single-fiber uses 1310nm and 1550nm wavelengths over the same fiber strand in opposite directions. The development of bi-directional wavelengths over the same fiber strand was the precursor to Wavelength Division Multiplexing.
In this application, two dual fiber switches are connected via single-fiber. Since BIDI single-fiber uses two separate wavelengths over the same fiber strand, the transmit (Tx) at one end of the fiber link matches the receive (Rx) from the other end, and vice versa.
Transponders
How to Use Transponders for Wavelength Conversion
Copper-to-fiber and fiber-to-fiber media converters are capable of wavelength conversion by using Small Form Pluggable (SFP) transceivers that transmit different wavelengths. SFP transceivers provide a convenient and flexible method of adapting to different equipment requirements.
For applications involving Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), copper-to-fiber converters can convert a copper interface to a specific WDM wavelength. Fiber-to-fiber converters provide a cost-effective solution to convert from standard optical wavelengths (850nm, 1310nm and 1550nm) of legacy equipment to optical wavelengths specified for WDM networks. Fiber-to-fiber wavelength converters are also known as transponders. Transponders are protocol transparent and can support Common Public Radio Interface (CPRI), Fibre Channel and Ethernet data rates.
WDM technology provides the flexibility to increase the capacity of existing fiber infrastructure, eliminating the need to lay new fiber at full capacity locations. Bandwidth is increased because each wavelength carries data independently from the others, allowing network designers to mix and match speeds (10Mbps up to 10Gbps) and protocols (T1, T3, OC-3, OC-12, Ethernet, etc) over the same fiber link.
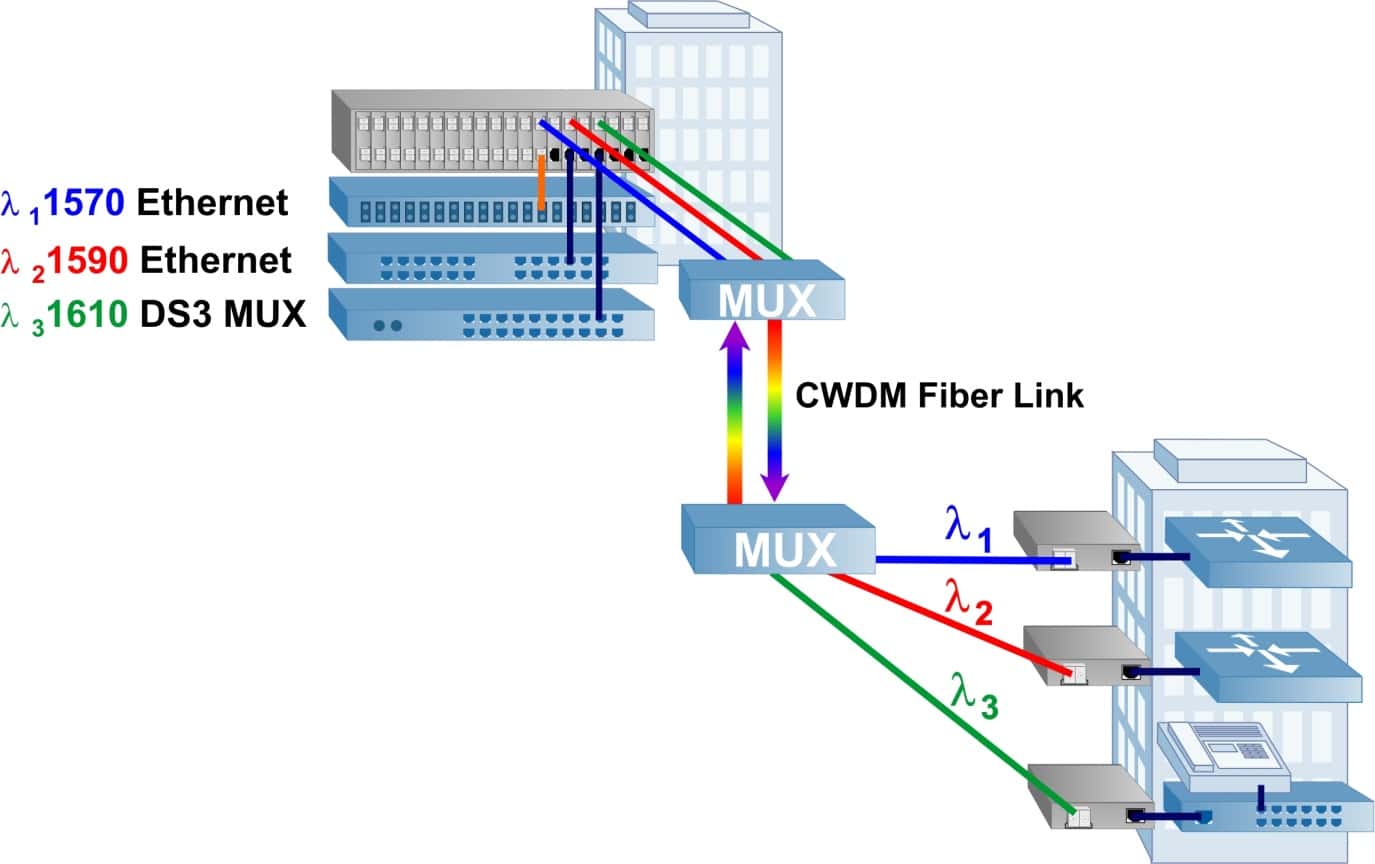
In this application example, an Enterprise network requires multiple devices and network protocols to be connected across a campus to another building. The challenge is that only one fiber link is available between the buildings. Utilizing media converters with SFPs and two WDM multiplexers (MUX), three wavelengths are sent over the same fiber link.
There is an Ethernet Gigabit fiber switch, a 10/100 UTP Ethernet Switch and a DS3 Multiplexer at the network core. The fiber switch link is converted from 1310nm to 1570nm fiber, the Ethernet UTP switch link is converted from copper to 1590nm fiber, and the DS3 Multiplexer link is converted from DS3 copper to 1610nm fiber. All three wavelengths are combined (multiplexed) into the WDM common fiber link.
At the other end of the WDM fiber link, the MUX filters out each of the wavelengths and provides connectivity to individual fiber links. At each link, a media converter with the appropriate wavelength SFP converts the fiber to back to copper. The two Ethernet links are connected to workgroup switches, and the DS3 link is connected to a PBX.